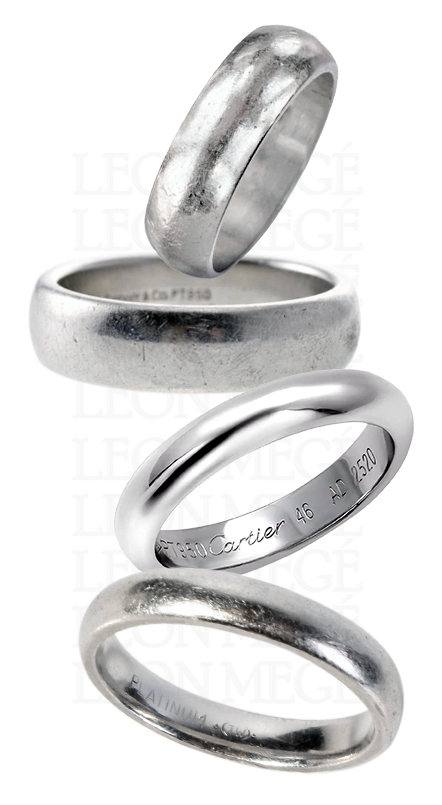
A wedding band symbolizes unity, signaling the opposite sex that you are no longer available. A classic wedding band is by far the most popular wedding ring style. It’s a traditional solid metal band featuring a gently curved outer surface and a flat inner surface with chamfered edges. Women tend to wear thin diamond-set wedding bands. Men gravitate toward masculine solid metal bands. We recommend wearing engagement and wedding bands on separate hands to avoid damage.

Case for wearing rings apart
Wearing a wedding band next to an engagement ring is a cause for concern and should be avoided. We advise wearing engagement and wedding rings on different hands to preserve their precious uniqueness and beauty. Of course, joining both rings for special occasions is OK, but continuous wear will inevitably wreck at least one.
The friction between two rings will cause damage, the extent and speed of which depends on the fit and how they stack against each other. The damage accelerates when the rings are too big for the finger, and there is a lot of movement. A tight fit and carefully selected band style can mitigate and slow the process.
Several factors contribute to the damage. A wedding band can eventually carve a tunnel through an engagement ring’s undercarriage. In time, it will appear to have been made intentionally. Consequently, the wedding band diamonds may fall out as a result of the engagement ring ripping off the beads holding them. Direct contact between diamonds causes the most extensive and usually irreparable damage. The friction will wear off the metal, weaken, and eventually break it unless two rings are permanently fused together. Although it eliminates friction, it turns the two rings into a single crooked ring with an offset center.
Comfort fit bands
A wedding band’s inner surface can be puffed up for easy sliding on the finger and a cushiony feel. It is a Comfort-Fit for Americans and a Court for the British. In contrast, the standard “pipe-cut” wedding bands are flat inside, lightweight, and cheap. A Comfort Fit band benefits those who take off the band frequently, such as medical professionals. Narrow wedding bands less than 3.0 mm wide do not cause discomfort and do not require Comfort-fit. A Light Comfort-fit is slightly less rounded, while a Heavy Comfort-fit has a bumpier curve. There is no uniform Comfort-fit profile; each manufacturer has a different template. All Leon Mege bespoke wedding bands feature our exclusive Effortless Glide™ edge that allows the rings to slip on effortlessly and stay tight on the finger, thanks to the smooth finish and soft chamfered rims for maximum comfort.

Wedding bands profiles
Classic wedding bands vary in depth, weight, and thickness. There are low, medium, and high dome bands. Alternatively, they might be called medium-weight, heavyweight, or extra-heavyweight bands.
In addition to depth, weight, and thickness, a wedding band varies in shape. The shape of its cross-section defines a band’s style and is called a “profile.” In theory, a wedding band’s profile can be any shape, but the most popular profile is the Dome shape or D-shape. A band’s width is easy to decide simply by trying it on one’s finger. The choice of the profile is a bit trickier.
A High Dome D-shape band’s maximum possible width is approximately 4.0 mm. Medium Domes are possible up to 6.0 mm in width, and a Low Dome can be made in any width.
The British Court profile is oval with a soft chamfered inner surface and truncated sides, which we call Comfort Fit.
Other British Court varieties include A Square (Flat) Court with a flat outer face, Slight Court, Flat-sided Court, Traditional Court, and Edge Court. The only one missing from this list is a Tennis Court.
A Cushion profile is similar to a Medium Edge Slight Court band. An example of that would be Tiffany’s Lucida band.
Flat or Rectangular bands range from 1.0 mm to 2.0 mm in thickness. They can be of any width. Their similarity to machine parts gives flat bands a more masculine look, often completed with a brushed finish.
Round or Halo profiles range from 1.0 mm to 3.0 mm in diameter and are essentially round wire twisted around a finger. Despite their simple look, Round bands are quite elegant.
Oval bands have a Low to Medium dome profile rounded to match the band’s curvature.
Concave bands are very European and have the shape of kidney beans.
Knife Edge bands are typically used as “spacers” and may feature millgrain on top.
Hinged - Articulated - Flexible bands
Are you aware that ring avulsions, also called degloving, are injuries to soft tissue like a ligament, tendon, or muscle when a wedding ring is suddenly pulled off or pressed hard against a finger causing bone, blood vessel, ligament, or nerve damage? There is also a possibility of sudden death from venous thromboembolism, a blood clot from poor blood circulation.
The hinged band’s flexibility offers a solution to this daunting problem. It has hinges that allow its sections to pivot when pressure is applied. The force gets redistributed, so there is less chance of injury. Each band consists of several links, usually between 3 and 8.
Articulated bands are extremely comfortable for anyone who routinely lift weights, be it dumbells or groceries, and those who find traditional rigid rings uncomfortable.
The pins can eventually wear off but can be easily refurbished.
Wedding band width and height
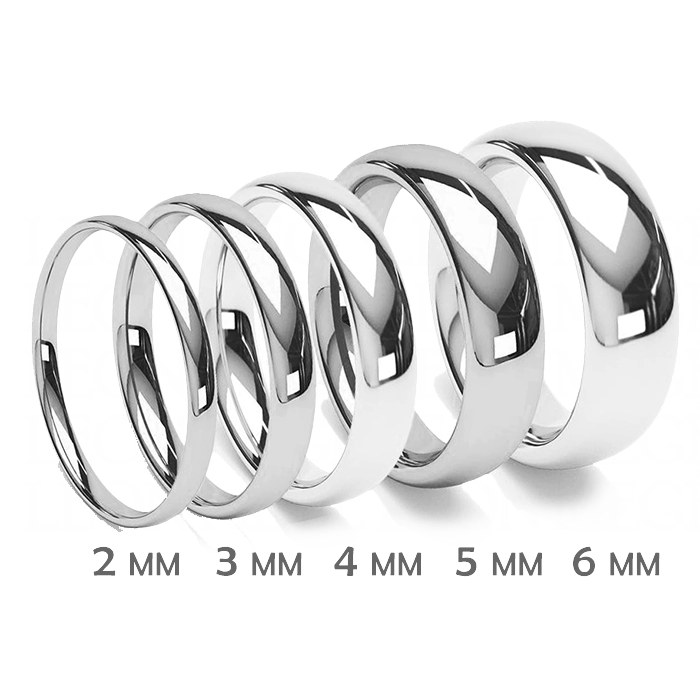
A band’s width is a matter of personal taste and cultural tradition. For example, in the US, men wear wide bands, and women prefer narrow wedding rings, while in some Eastern European countries, the opposite is true. A classic wedding band with its traditional domed profile is the most popular wedding band for men. Men’s bands range from 1.0 to 15.0 mm wide. In the US, men go for 3.0 mm and wider bands, while women prefer a width of 2.0 mm or less.
A band’s width correlates with the finger’s size: a 4.0 mm finger size six band would look too bulky, yet scaled to finger size 16, a 4.0 mm band would look too narrow. 1.0 mm of width compensates for an approximate increase in 3 finger sizes. It means that 5.0mm size 14 and 3.5 mm size nine bands have a similar look on the finger.
Wedding bands are measured by height, sometimes referred to as depth, and by width. The term thickness is confusing because it could mean both width and height. The band’s height starts from the finger and extends to the top. Wedding bands are typically less than 2.5 mm high to prevent discomfort during wear, determined by their width and desired profile. Wider bands have a lower profile to avoid getting uncomfortably high.
- High dome bands ranging from 1.0 mm to 4 mm wide are 1.2 – 1.5 mm thick
- Medium dome bands ranging from 2.0 mm to 6.0 mm wide are 1.6 – 2.0 mm thick
- Low dome bands ranging from 2.0 mm to 10.0 mm wide are 2.1 – 2.5 mm thick.
Wedding bands’ widths range from extremely thin, less than 1.0 mm, to extra-wide, 15.0 mm, or even more. The band’s width affects the comfort as well as the fit. Wide rings feel tight on a finger because they displace more skin.
Wedding band finishes

There are two basic types of finishes – shiny and textured. The shiny surface is achieved by gradually reducing scratches, pits, and other blemishes until the metal is spotless and smooth. A texture can be added during or after the polishing is done. It’s best described as “controlled scarring.” When it comes to different finishes, there is no universal terminology. Don’t be surprised if one jeweler’s satin is another one’s brush.
Properly made bands have a texture only on the outside and never on the inside.
The contrast between polished and textured surfaces dramatically clarifies that texturing is intentional and not resulting from poor craftsmanship.
Here’s an extensive list of finishes available for your wedding band:
High polish is a crisp, bright polish with high-contrast reflections and without foggy spots. 1-2 micron precision is required for the perfect mirror-like finish (Source: “Kruger’s Guide to Industrial Smoothing”). The polish’s brightness depends on metal density and hardness. High luster is impossible on soft, unalloyed metal or a spongy, low-density casting. High polish is best at revealing the luxurious shine of hand-forged metal.
Bright polish is the most popular choice among most women and men. 99.5% of women and 92% of men choose a bright polish for their wedding bands.
Zaratsu or Black polishing can be done on flat surfaces of hard metals (for example, stainless steel) that are polished to a distortion-free, brilliant mirrored finish. It is done by firmly pressing the metal part against a spinning tin wheel primed with finer and finer abrasives. Typically used in the watch industry.
Matte is technically not a texture but a dull polish. Matte is the early stage of polishing a piece to a high-luster finish.
The Satin finish is very fine and smooth. It resembles a surface of silk. The satin finish comprises hundreds of microscopic lines that are invisible without magnification. The satin finish is often achieved by scorching a polished surface with steel wool glued to a handle.
The Iced finish resembles a surface of an ice-skating rink after a hockey match.
The Brushed finish is achieved by manually applying one-directional strokes or using a rotary wheel with abrasive sandpaper. The finish is made of uniform scratches, and their coarseness depends on the grade of sandpaper used.
Stone or Bark finish is a rough, dented surface with a random granular feel. Typically it’s done by leaving the cast surface raw. This finish is popular with pretentious amateur jewelers unable to machine the casting to a clean, crisp finish.
Sabi finish, a Japanese word for “beautiful,” is a coarse finish accomplished by making deep parallel scars with a knife-edge burr. The Sabi finish was named and popularized by the legendary jewelry designer Henry Dunay.
The Florentine finish is a pattern of etched lines crossing each other at a 90-degree angle. The technique makes the metal surface resemble fine fabric or course textiles, depending on how coarse the lines are. A special graver that cuts multiple parallel lines in one stroke can produce the finish. The Florentine finish features prominently in Buccellati jewelry, among many others. Florentine finish’s popularity began fading away in the 1980s.
The Hammered finish has an appearance of a rough, crudely forged surface. The dents are machined with a cutting tool rather than by hammering.
The Acid finish is achieved by applying harsh chemicals that leave thousands of microscopic pits on the surface. It’s a quick way of finishing jewelry on an industrial scale. Frost finish is an alternative name for the acid finish, albeit more poetic.
Sand or Sandblasted finish is a result of blasting the surface with a stream of an abrasive powder. The finished surface resembles a coarser version of the acid finish. Blasting is done under high pressure in a sealed enclosure to prevent inhaling since breathing pulverized sand can lead to a severe medical condition known as silicosis.
The Corrugated finish is a rough ridged surface with irregular trenches gouged at a 45-degree angle. This bizarre texture is found on low-end jewelry and never in fine jewelry.
Granulation is a recently revived ancient technique of assembling decorative patterns from tiny gold beads soldered to the surface.
The Honeycomb finish is a hexagonal relief etched on the surface.
The Knurling is a diamond-shaped (criss-cross) pattern imprinted on a surface to ensure a better grip. Occasionally it is confused with millgraining.
The Distressed finish is an artificially induced aged appearance achieved by rubbing or scorching the band. This is a natural finish that any plain wedding band eventually achieves during normal wear.
The Perlage consists of small, overlapping concentric circles produced by a rotating metal brush.
The Glashütte ribbing is produced by mechanical means. It emulates a gently rippled effect.
The Sunray finish is a spiral pattern typically covering large surfaces in watches.
Hand engraving is a form of artistic etching. Engraving can be replicated during casting, as is done in low-end jewelry. A pattern can be milled using a CNC machine or a laser, but the results are always mediocre. Only when done by a master artist does the ancient art of hang-engraving look terrific. Custom engraving is expensive as it takes a long time, but it’s worth every penny.
Micro-pavé is a surface embedded with small diamonds or gemstones, each serving as a tiny tile. The combination of stones and metalwork is a composite material with a characteristic texture.
Milgrain edge
A milgrain wedding band has an old-fashioned, conservative Ivy League Country Club look that instantly sets you apart. Imprinting a row of tiny beads or semi-spheres on top of sharp edges blunts the edge, conceals uneven spots, and enhances the design by giving it a lacy appearance. Contrary to the writings of some dimwit jewelry bloggers, the word milgrain does not translate to “a thousand grains” in French. The French call it grisant, meaning shaded, greyed out, or dull edge.
Milgrain is done by rolling a special tool along the sharp edge. In tight spots, milgrain is fashioned one bead at a time using a graver. Imitation milgrain is cast from a mold or a CAD model. It’s vastly inferior to hand-applied milgrain.
Milgrain comes in different sizes ranging from #1 to #15 (0.1 mm wide to 1.5 mm wide). The large milgrain on a dull wide edge resembles reeding on the coin’s edge. The finer and prettier the milgrain, the faster it wears off and disappears, leaving a dull, flattened border in its place. The milgrain can be applied mechanically using a hand-cranked Millrite lathe/vise contraption.
Milgrain is short for “milled beads” or “imprint of grains.” There are alternative spellings of the word: “millegrain,” sometimes “millegraine,” but most often, the term is “millgrain” or “milgrain.”


Halfway set bands
A wedding band encircled with diamonds has a deep meaning. A wedding band symbolizes a marriage lasting for eternity. A marriage license never expires, and so does the endless row of diamonds. In addition, a partially-set band is tacky. It is the jewelry equivalent of Howard Wolowitz’s backless dickey shirt. Contrary to mistaken belief, a halfway-set band turned upside down will not protect from criminals looking to rob someone.
Best metal for wedding bands
Platinum is perfect for bridal jewelry whose purity resonates with the sanctity of marriage. Choosing the right metal is personal, and each material has advantages and disadvantages, but platinum always comes out on top thanks to its rarity and resilience. Platinum has always been a preferred metal for bridal jewelry because of its naturally soft white color and beautiful luster. Its neutral color that doesn’t tarnish or oxidize makes color coordination a snap. Platinum is almost twice as heavy as gold. It feels substantial and constantly reminds you of your marital obligations with its presence. Aged platinum develops a dignified, noble patina, a unique appearance, impossible to reproduce mechanically, best described as distressed “shabby chic,” reminiscent of shimmering rustic silverware punctuated by microscopic dings.
White gold is not an ideal choice for a wedding band. White gold was created as a platinum substitute during the war when platinum was considered a scarce strategic asset. White gold is usually plated with rhodium to conceal its yellow tint.
A thin layer of rhodium (a white metal in the platinum group) is applied to the surface, giving white gold its bright white shine. Rhodium is very hard, so it provides a degree of protection from scratches until its thin layer wears or peels off. That’s why white gold jewelry must be “dipped” repeatedly to reapply rhodium.
Some jewelers falsely claim that their white gold alloy is so white that it does not require rhodium plating. It’s not true; all white gold alloys have approximately the same hardness. Consumers are also often misled into thinking white gold is harder than platinum. This is false; platinum is harder.
The short answer is no, yellow gold’s popularity is on the decline. Historically, gold’s rich yellow color was a significant draw. However, women and men have been shunning yellow metal for many decades now. Gold is not making a comeback in bridal jewelry. Today, it’s more and more a symbol of excess and extravagance.
In an episode of the popular Sex and the City, the yuppy icon, Carrie Bradshaw, dry heaved at the news that her boyfriend was about to get her a gold ring. If you want a warm metal color for your wedding band, consider pink gold instead of yellow.
In the last decade, gold cost almost twice as much as platinum. There are several reasons why gold bands are cheaper:
- Platinum is much denser; the same band weighs almost double when it’s platinum.
- The platinum alloy contains 95% pure platinum, while 14k gold has only 58.3% of pure gold.
- Platinum is usually combined with ruthenium, a platinum group metal, while gold is alloyed with inexpensive copper and zinc.
- Platinum wedding bands are more difficult to manufacture as they require special skills and expensive machinery.
Once more valuable than gold, silver has been prized for centuries. Its relative softness has hampered traditional use for making wedding bands. Silver also tarnishes very quickly.
Pure silver is too soft to be used in jewelry; it must be alloyed with copper to boost its strength. Sterling silver contains at least 92.5% of pure silver. On the positive side, silver does protect from vampires.
Pink gold is an upscale alloy associated with wealth, glamour, and grandeur, minus the glitz and extravagance of its yellow cousin.
Pink, red, or rose gold (the same thing, rose sounds more romantic) is highly durable and resistant to scratches and dents. It owes its beautiful tender color to a higher share of copper in its alloy. Copper is also responsible for rose gold’s exceptional hardness that makes high luster polish possible.
Rose gold owes its prominence to Russians who used it in all types of jewelry, starting from Carl Fabergé’s famous Easter eggs to tea kettles for wealthy merchants. In Russia, up until very recently, pink gold was considered the natural gold color, earning it a nickname “Russian gold”. There are a few drawbacks – even 18k rose gold tarnishes fairly quickly. It is also more difficult to hand-forge.

What do Presidents and Royalty wear?
Traditionally, the British Royal wedding bands, including the one Queen Elizabeth II, wears, are fashioned from rare Welsh gold. It sits behind her engagement ring set with diamonds ripped from her late husband’s mother’s tiara. Prince Charles wears a gold signet ring layered with his Welsh gold wedding band on his left hand’s little finger in a medieval fashion. Is it a sign of his individuality, as he claims, or a clever life hack to halt the finger from sliding onto his enormous schnozzle?
 Duchess Camilla’s gold wedding band paired with her gangsta-size diamond doesn’t distract from her Rottweiler features.
Duchess Camilla’s gold wedding band paired with her gangsta-size diamond doesn’t distract from her Rottweiler features.
Princess Diana wore a Welsh gold wedding band until the Firm arranged for her fatal ride.
In a bold move, follically deprived Prince William decided not to wear a gold wedding ring when he married Kate Middleton.

Meghan Markle’s wedding band is made from the same Welsh gold stash used for royal rings. Prince Harry’s platinum wedding band has a textured finish that pairs well with Nazi costumes.
Princess Eugenie caused a stir when her Welsh gold wedding band was too tight for her souped-up fingers during the wedding ceremony.
After three years of dating, Nancy Reagan was married to Ronald for 52 years. She didn’t wear an engagement ring, but she wore a platinum diamond wedding band.
Hillary Clinton reportedly turned down an engagement ring in favor of pork futures. She and Bill exchanged family heirloom wedding bands.

Mr. Obama’s wedding band was a thick, carved gold band from Indonesia, where he lived from age 6 to 10. The conspiracy theory that Mr. Obama’s wedding ring was inscribed with the first half of the Islamic declaration of faith, the Shahada: “There is no god except Allah,” is a hoax.
Melania Trump wears a 13-carat platinum eternity band with fifteen emerald-cut diamonds. The rumors of a Q diamond color are baseless. Supposedly, Donald bartered the $200k Graff eternity band worth $1.5 million for TV promotions on The Apprentice.
Celebrity wedding bands
A quick look at celebrities gives us a great insight into the broad scope of wedding band styles. They rip through scores of marriages faster than fire through a box of matches. Each marriage has a wedding band that is different from the one before. Celebrities have a pompous habit of attributing deep spiritual meaning to their jewelry to justify their extravagant vanity. The PR helps with landing cushy movie roles without visiting Weinstein’s stained couch.
During a secret civil ceremony, Joe DiMaggio presented Marilyn Monroe with a platinum channel-set band with 36 baguettes. It wasn’t her only wedding ring, but it was sold for $772,500 at Christie’s in 1999, even though one baguette went missing. An astonishing price for the mediocre band worth less than $20,000 even today. It took about a baguette per week to keep the two American icons in an enduring romantic relationship that lasted only nine months.
Before Jennifer Lopez’s marriage ended in divorce, she often ditched her gold wedding band because it just didn’t go with her platinum rings. Most fashionistas agree that mixing gold and platinum jewelry is a big no-no.
Before her divorce from Kanye West, Kim Kardashian wore an ultra-thin platinum micro pave band – a surprisingly understated piece for her luscious form.
Carrie Underwood wears a curved diamond wedding band to accommodate her engagement ring. The platinum shadow band is said to be as unique as her singing style.
Scarlett Johansson wears a thick gold wedding band as per the Russian heritage requirements. Russian women favor bands as wide as a truck tire.
Chris Pratt wears a plain gold wedding band. In the movie “Passengers,” his character crafts a wedding band using platinum stripped from the spaceship’s fusion reactor. At least, that’s what they want us to believe. We think he steals the ring from a jewelry boutique onboard.
Adam Levine got a plain platinum band for himself and a finger tattoo for his Namibian-born shiksa. “The tattoo is still there when I take my engagement ring off,” she said. “Wow, that was cheap,” he thought.
Amal Clooney’s dainty micro pave band sits flush against the platinum engagement ring she got from George. It’s not a million in a Tumi bag that each of his pals got from him, but still a nice gesture.


Alternative materials
Gold, silver, and platinum aren’t your only metal options when buying a wedding band. From traditional to ultra-modern, there are plenty of materials to consider.
Palladium is a naturally white metal that is visually indistinguishable from platinum. It is one of the rarest metals on Earth. A decade ago, palladium was considered a cheap platinum substitute, costing a fraction of platinum’s price. Today, palladium is twice as expensive as platinum. Even Bitcoin millionaires will think twice before ordering a band made out of palladium. Palladium is lighter than platinum, very durable, and hypoallergenic.
Titanium is among the strongest and most lightweight metals for wedding bands. Those exhausted from wearing heavy platinum bands can finally be relieved by titanium’s almost plastic-like heft.
Stainless steel rings are strong and cheap. They can be polished to a shiny chrome finish or brushed for a pewter look. Either way, you’ve got yourself a shiny piece of hardware.
Damascus steel rings are made of two alternating types of stainless steel layered together to create striped patterns. Some layers are chemically darkened to add a dramatic contrast similar to zebra skin.
Meteorite iron is often incorporated in wedding bands combined with other metals, such as titanium, platinum, and gold. Stellar-born superheated meteorites fallen on Earth slowly cooled over billions of years, causing iron molecules to settle into a crystalline Widmanstätten pattern that does not occur elsewhere on Earth. Tungsten, or Wolfram for Krauts, is a silvery metal identified as a new element in 1781. It is four times harder than titanium and hypoallergenic but, unfortunately, prone to shattering. Because of their hardness, tungsten rings have a brilliant, vitreous shine.
Tungsten rings cannot be sized, but this is rarely an issue. Tungsten rings are very inexpensive and can be easily replaced.
Cobalt is a bright white metal known as “poor wife’s platinum.” It is heavier than other non-precious metals, which gives it a substantial feel. It’s perfect for those who want to always keep in touch with their wedding vows.
Ceramic wedding bands may look cool at first, but they are more appropriate for teenagers. They are so cheap that you may want to marry a few more times to enjoy the bargain.
Wood can be found in wedding bands as an inlay in titanium, ceramic, or tungsten. Whole rings may also be carved out of a solid piece of wood. These rings are not indestructible and require extra care to stay presentable. On the plus side, they’re dirt cheap.
Dinosaur bone rings contain fossilized bones of Barney and his friends. His remains are cut up and used for inlays combined with meteorite iron, exotic wood, or other equally fascinating materials. A grim reminder that our remains might end up in family court one day.
Zirconium is a grayish-white metal that is similar to titanium but has a ceramic-like feel to it. Zirconium is shatter-proof, relatively lightweight, skin-friendly, and cheap. Zirconium darkens when exposed to oxidation, so zirconium bands are usually jet-black. Zirconium is used in nuclear reactors due to its high heat and corrosion resistance, so it’s a safe bet that Homer Simpson wears a zirconium band.
Antlers of many different species, colors, and textures are used as an inlay material in wedding bands, serving as a constant reminder of senseless animal murder. Some animals died before their remains were dug out and desecrated.
Carbon fiber is a very lightweight, durable material made from organic polymers. These wedding bands are made entirely from carbon fiber or used as inlays. Carbon fiber rings are pretty durable and cheap.
Mokume gane style
Mokume-gane is a highly specialized technique perfected by the Japanese of imitating wood-like texture on a metal surface (hence the name: mokume – wood grain and gane – metal 木目金 ). Various metals and alloys are fused to produce a laminate with a uniquely patterned finish. This stock is used for making wedding bands.
Denbei Shoami, a Japanese metalsmith, is credited with inventing the technique for decorating samurai swords. Like wood graining caused by naturally alternating harder and softer layers of wood, the patterns in mokume gane are due to each metal’s different physical properties – hardness, toughness, resistance to corrosion, etc. As pretty as they are when new mokume gane bands quickly deteriorate and lose their look. They generally cannot be sized and cost too much for a novelty item.
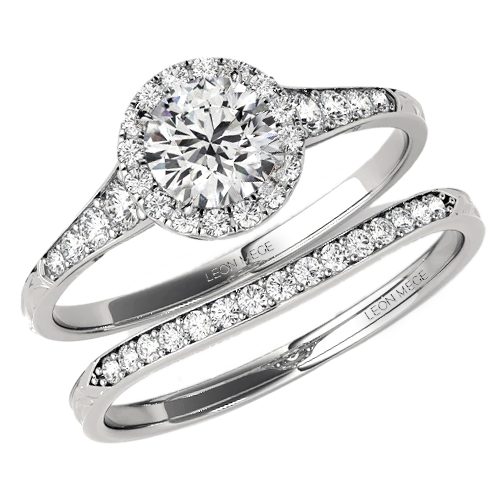


Shadow wedding band
A shadow wedding band has a curved section that fits flush next to an engagement ring. Useless on its own, the band has many different names such as “curved band,” “fitted band,” “molded band,” “custom shaped band,” or “waveband.” The aesthetically challenged wavy band looks awkward and makes no sense as a symbol of marriage.
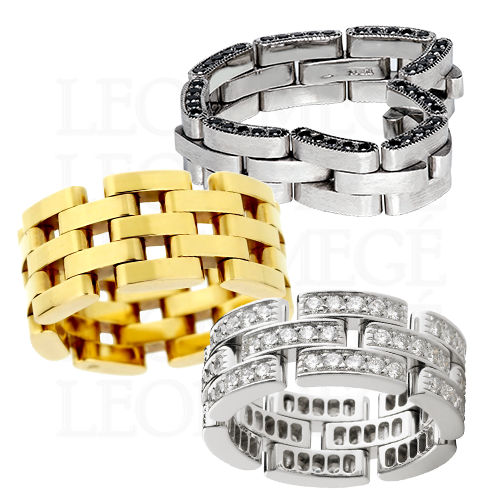
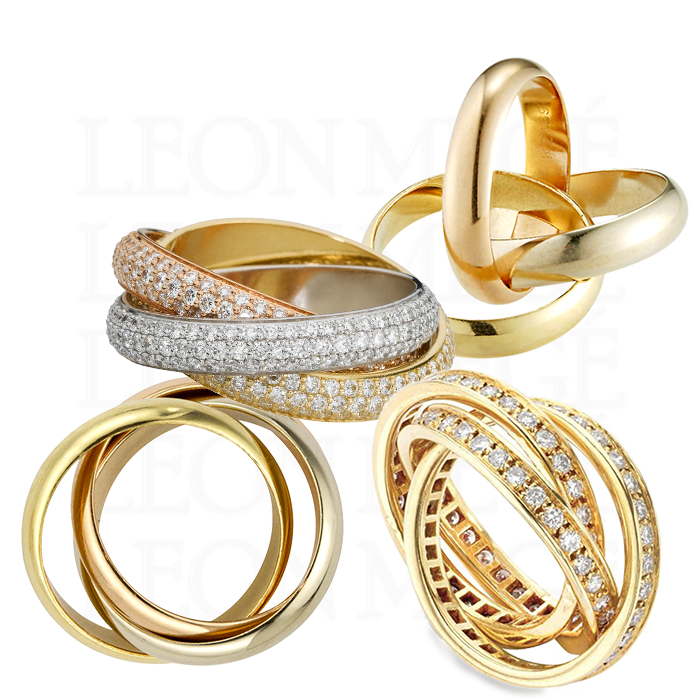
Cartier "Rolling band"
The “Rolling” band is a name coined by Cartier for interlinked multicolored bands symbolizing all aspects of a relationship: white is for friendship, pink is for love, and yellow is for fidelity. Each band, a set of several, usually three, is connected to the other two, allowing them to slide on the finger easily by rolling over each other. The Cartier Trinity band is one such example. A rolling band finger size cannot be measured on a ring stick – it must be tried on.
According to legend Jean Cocteau saw Saturn’s rings in a dream, and his friend Louis Cartier turned the dream into a reality circa 1924. The ring design existed long before Jean and Louis went interstellar; such bands were commonplace all over Eastern Europe. However, Cartier beat Russians and Poles to the punch expropriating the design to call its own.


What makes Leon Megé's wedding bands unique?
The mathematically derived templates developed by Leon Megé over decades of research maximize elegance and comfort in the final product. Leon Megé bands are distinguished by refined lines: precise, elegant curvatures that determine the look of any classic wedding band.
Leon Megé forges traditional, upscale wedding bands from high-grade platinum, sealing rough spots with a high-frequency laser beam. There are no soldering joints or casting seams.
Leon Megé’s bench-made classic wedding bands are available only to customers who have purchased an engagement ring from us.
Women overwhelmingly prefer wedding bands set with diamonds over plain metal bands. Even the Orthodox Jews required to wear a solid band at the wedding ceremony often set it with diamonds once the nuptial formalities are out of the way.
The choice of a wedding band depends on how the wedding band is worn. The majority of women wear engagement and wedding rings on the same finger. This eventually causes damage from friction to both rings, so we don’t recommend it.
For those who wear both engagement and wedding rings together, a pave-set band makes the most sense. A pave band works with any engagement ring regardless of the diamond’s shape.
There are two basic styles: soft blurry outline of modern pave, and bright-cut pave with well-defined rigid edges. Engagement rings with emeralds or Asschers are complemented by bands with a bright-cut pave. A modern-style pave works well for rounded stones such as ovals, cushions, pears, marquises, and, of course, rounds.
A thin low-sitting wedding band is key to minimizing friction. The choice of a bright-cut style pave offers better protection than a modern pave. A thin, dainty pave band will stay closer to the engagement ring without a large gap in between. It’s recommended to keep the band’s width to the minimum since a wedding band should not compete but rather complement the engagement ring.
For those who wear engagement and wedding rings separately, the possibilities are endless. A woman can wear a more substantial wedding band with larger stones without potentially overpowering her engagement ring. Any diamond shape or a combination of shapes is fair game. Larger stones can share prongs, hence the name “shared-prong” bands. Eternity bands can also be bezel or channel set.
To tie both rings stylistically, pair a step-cut diamond with a step-cut-set wedding band, while a brilliant-cut band can accompany a brilliant-cut engagement ring.
A puzzle ring is made of disfigured links assembled tightly together so it appears solid. Once the rings have been dislodged from their places, it’s up to the wearer to solve the puzzle. The rings can be reassembled by turning each piece in a certain way following a predetermined sequence of steps. Directions for solving rings’ puzzles are usually supplied. Patience is required because forcing, compressing, or bending the parts will destroy the ring.
Puzzle rings are rarely used as wedding bands, but when they do, they can prevent cheating. The mechanism of how it works is unknown, but based on the historical records, Middle East rulers used to require each of their wives to wear a puzzle ring to guarantee her fidelity.
Puzzle rings were invented at least 2000 years ago and appeared in Europe during the Renaissance. They remain popular in the Middle East. When you travel to Damascus, pick up a puzzle ring at the Souk El-Hamidiyeh shopping center. While you are there, pick up a scoop of ice cream at the venerable Bakdash ice cream parlor.
A ring jacket, also called a ring wrap, a ring enhancer, or a ring guard, is an old-fashioned concept that’s gone out of style but is still being used today.
A jacket is made of two connected shadow bands with a space in the middle where an engagement ring can be dropped. A ring jacket is usually a way to add a “dressier” option to an engagement ring. It also adds stability to the ring and reduces spin. A ring jacket makes it possible to update the look of a unique engagement ring without changing the ring itself.
Using a ring jacket as a wedding band is a no-no. You cannot wear it without the engagement ring, and it looks like a part of the engagement ring when worn together.
Any band can be used in a stack, including most wedding bands. The key in assembling a stack is using bands that are approximately the same height so that none stick out.
A stack allows you to mix bands in many arrangements according to your mood, occasion, or dress. A stack of bands is popular, fashionable, even trendy. Adding a wedding band to the mix is a fun way to add more flexibility without buying more rings.
Unless an heirloom band stayed in the family for generations and has sentimental value, there is no reason to re-use someone else’s ring.
There are two reasons for a used wedding band to be sold: whomever it was made for, it didn’t work, or its owner passed away, and the surviving party did not feel overly attached. Do you want this twisted karma to affect your eternal happiness? We all know that curses and jinxes are silly superstitions but would you like to spend your married life proving that?
Unlike an engagement ring, a wedding band is usually not that expensive. If you cannot afford gold or platinum, get a silver one. Still too expensive? Steel, wood, or ceramic bands are super cheap.
A wedding band is worn nonstop, so ensuring it’s entirely safe for your skin is a priority. “Hypoallergenic” metals are those that are least likely to cause an allergic reaction. All metals except platinum can cause an allergic reaction.
Moisture from frequent hand washing or swimming can be a possible cause of skin irritation. Perspiration, lotions, and household chemicals trapped under the wedding band can also cause irritation. Cleaning your wedding band regularly and drying it thoroughly after washing your hands can rule out allergies. If you continue to have irritation caused by your wedding band, consider getting a divorce.
Nickel, zinc, copper, and lead used in metal alloys can cause allergies. Nickel allergies are prevalent and quite severe. European Union bans the metal from use in gold alloys. Unfortunately, the majority of white gold jewelry sold in the US is made with nickel alloy. It is worth noting that Leon Mege jewelry is never made using nickel alloy. If you are aware of any metal allergy that you might have, you can contact us to make sure the ring you’re interested in is safe for you.
Since the human body does not react to platinum and palladium, these metals are used for biomedical applications. Both are completely safe for people with sensitive skin. Platinum is 75% denser than palladium and 20 times as dense as water. Palladium is a precious silver-colored metal very similar to platinum in appearance. It’s almost as light as gold but more pliable. Both metals can be formed into virtually any shape and suited for all jewelry applications.
Yellow gold is generally hypoallergenic if it contains a minimum of 75% of pure gold – 18k or higher. Copper and silver used for alloying gold rarely cause adverse reactions, but zinc occasionally does. Gold alloys are significantly less hypoallergenic than platinum or palladium. White gold should be avoided because there is a strong chance it contains poisonous nickel.
Cobalt is a scratch-resistant, cheap, dark silvery metal used to make wedding bands. It is used in dental and orthopedic implants for its hypoallergenic properties and durability. You can also consider surgical stainless steel, whether it fell from the sky in meteorites or was melted by humans. Stainless steel wedding bands are cheap and safe to wear. When everything else fails, consider zirconium – a lightweight and hypoallergenic material. You can’t go cheaper than that.
Retailers love matching wedding band sets and what’s not to love – two sales with one sales pitch. A matching set usually consists of two same metal but different styles bands or similar style bands in a different metal. When the couple is together, matching bands are so sugary sweet you can get diabetes just by looking; when they are away from each other, nobody will know anyway.
His’n’her’s wedding band sets are popular in Europe, where couples are not embarrassed to wear identical rings. Such conformity of tastes between a man and a woman is unhealthy. Women deserve something more special, beautiful, feminine. Men require something more masculine and straightforward.
There are exceptions, of course, but we advise dismissing the idea of a wedding band matching set. Show your individuality! Otherwise, we end up marching in goose step, wearing identical Hugo Boss uniforms and saluting each other with the right arm extended at a 30-degree angle.
Zirconium, titanium, and steel rings can be cut off from the finger by medical personnel, but it’s a major headache, so medics will not appreciate your taste in alternative metals.
The hardness of platinum and white gold alloys is based on the Vickers scale (HV). The higher number indicates a more rigid metal. There is a significant difference in hardness between hand-forged (cold worked) metal and metal produced by casting.
How metals stack up from the softest to the hardest:
110 HV – 5% iridium platinum cast – incredibly soft, not suitable for hand-forging
130 HV – 5.0% ruthenium platinum cast
135 HV – 4.5% cobalt platinum cast, the relatively soft magnetic alloy used in mass production
150 HV – 18k yellow gold cast
190 HV – 18k palladium white gold cost
210 HV – 18k hand-forged yellow gold is used for bench work. High-end jewelers use 18k gold exclusively.
216 HV – 18k palladium hand-forged white gold. This alloy is rarely used because of palladium’s high cost. Platinum is the better option.
220-230 HV – 5.0% ruthenium hand-forged platinum. Used in high-end jewelry. All Leon Megé jewelry is made using this alloy.
220 HV – 18k nickel white gold. This alloy has a significant yellow tint. May cause severe allergic reactions. Illegal for use in jewelry in the European Union.
350 HV – 14k nickel white gold – rock-hard, dangerous, pale yellow, allergy-causing alloy, illegal in the European Union.
There are many different types of wedding bands unique and memorable, and there is hardly any need to personalize them.
For those whose ego yearns for more, hand engraving or setting a secret birthstone is a solution. Both are popular and affordable options for adding a personal touch to a wedding band. An engraved wedding date can also help to avoid the embarrassment of forgetting an anniversary. There are also various novelties, such as a digitally enhanced fingerprint molded on the band.
Very thin, flat bands can be used to separate a wedding band from an engagement ring to avoid damage from friction. This is a viable option if both rings have pavés, especially on the sides where they would be touching.
A spacer can also be added to a stack as an accent to vary the mix.
The art of decorating metal by incising a pattern of grooves onto its surface is called engraving. An engraving can be an inscription or a pattern. Cheap machine engraving, the type used for personalizing trophies or dog tags, is done with a marking machine or a laser.
Genuine engraving is done by hand using a special tool made of tempered steel. It’s called a “graver” (“burin” or “échoppe” in French, “stichel” in German). A professional engraver is an artist who uses metal as a medium. Precise work on a microscopic scale is challenging. Very few people are capable of such meticulous craftsmanship.
A hand inscription is an excellent way to make a wedding band special. An inscription is usually hidden inside the ring. On occasion, it can be on the outside for the whole world to see.
Engraving is done when the band is finished and polished. Therefore, it’s a good idea to try the band to ensure the perfect fit. Adjusting the size can damage the engraving, so it might need to be re-done. Decorative engraving is done to hide and beautify exposed metal surfaces. It is often done on the top and the sides of a band.
An engraving slowly wears off over time. It can also be damaged during ring sizing. An engraving can be restored, although an inscription tempered by time radiates a more profound meaning and should be left alone.
Wedding bands often carry a personal inscription immortalizing the couple’s feelings towards each other. Usually, it is a line from a poem, a verse from a favorite Holy book, a Chinese letter from a takeout menu, or anything else deeply meaningful to both parties.
The limited space inside the band already taken up by stamps and hallmarks calls for a short, abbreviated version of an endearment. A couple of short words will do.
Engraving the wedding date is popular and even helpful. It can prevent those embarrassing moments in a couple’s life when a spouse forgets an anniversary.
The inscription is meticulously carved by a professional using a special tool. It is tedious and expensive, but the result is entirely different from cheap machine engravings you get at the mall.