
Ruby is a red variety of mineral corundum. All other corundum colors, including pink, are called sapphires. Rubies are by far the most precious gemstones that are stunning to behold and rarer than diamonds. Ruby’s vivid color was frowned upon in the drab ’70s. Today red is a badge of solid personality, intellect, and success. Rubies are a true statement of personal style and sophistication.
The diamond market is controlled by De Beers Société Anonyme, manipulating the market supply and controlling the prices. Rubies do not have an international monopoly to lean on. Therefore, the perception that diamonds are rarer than rubies is not accurate.
Corundum crystals are found in nature in every color and even completely colorless. Sapphires and rubies are the same stones colored by different impurities.
- Mohs’ Hardness: 9
- Specific Gravity 3.97-4.05
- Chemical Composition Al2O3
- Refractive Index: 1.762–1.774 (0.008) Uniaxial negative
- Crystal System: Hexagonal (trigonal); dipyramidal structure, barrel-shaped, tabloid-shaped
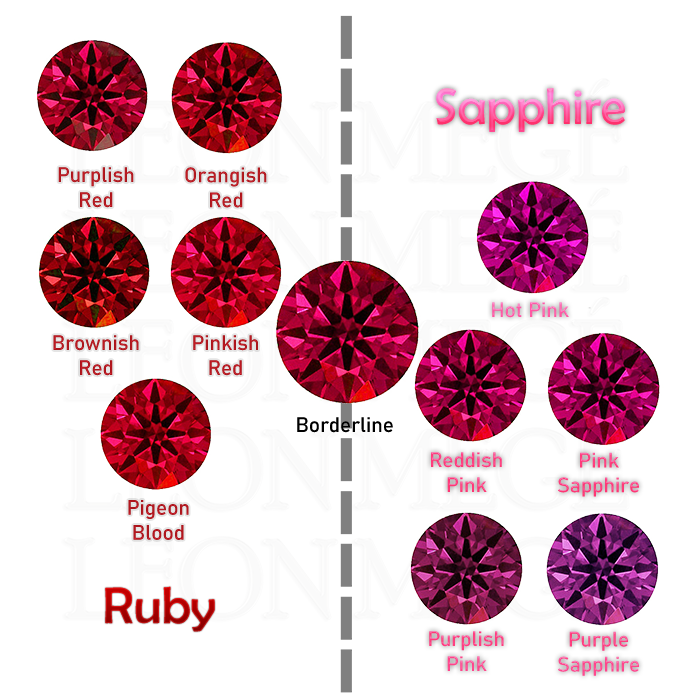
Ruby vs. Pink sapphire
Rubies and pink sapphires are distinguished by the saturation of the red hue and the strength of blue and yellow undertones. The presence of chromium causes the color of a ruby, while a combination of chromium and iron causes the color of a pink sapphire. Chromium, iron, or titanium impurities are responsible for most color variations. Rubies and pink sapphires can be distinguished by their clarity. Rubies tend to have more imperfections than pink sapphires. Rubies are more valuable than pink sapphires. This is because rubies with a saturated pure red color are extremely rare.
Pigeon Blood rubies
Exceptional rubies with a pure red color are the most coveted gems. They are known as “Pigeon Blood red” rubies that, aside from their distinct color, invariably are stones of superior quality.
“Pigeon Blood” is a historic term used for centuries by the jewelry trade to describe the finest rubies from the Mogok mine in Burma (Myanmar). For a ruby to qualify for the term “pigeon blood red,” the color must be an intense, saturated, and uniform red with vivid internal reflections. Their saturated red color without a hint of blue or brown is intensified by strong fluorescence caused by a lack of iron impurities.
Any treatment (heating, fissure filling, etc.) disqualifies a stone from being described as “pigeon blood red.” The stone must be a transparent crystal without eye-visible or dark inclusions. In addition, it must show a homogeneous color distribution with vivid internal reflections.
Burmese rubies ban
The international trade in valuable Burmese rubies and jadeites has been under political sanctions since 2003, aimed at applying pressure on the communist junta. The embargo banned all gemstone imports from Burma with one loophole – stones could be legally imported if polished outside Burma, usually Thailand. In 2008 the Bush administration introduced legislation banning Burmese ruby and jadeite trade regardless of processing location.
With the normalization of relations between the US and Burma in 2012, the Treasury and State Departments announced that they were lifting sanctions on a range of Burmese products, but not ruby and jadeite. However, in August 2013, President Obama signed an executive order that renewed the ban on importing Burmese ruby and jadeite for another year. Finally, in October 2016, President Obama signed an executive order to lift all remaining Burma sanctions, including the Burmese ruby and jade ban.
However, after ten years of democratically elected governments, the military in Myanmar arrested the democratically elected government, declared a state of emergency, and handed all powers to the army chief.
In 2021 the Biden administration banned US companies from dealing with three Myanmar gem producers associated with the Burmese junta: Myanmar Ruby Enterprise, Myanmar Imperial Jade Co., and Cancri Gems and Jewellery Co. The sanctions did nothing to the Burmese junta supported by Chinese and Russians who keep buying ruby and jadeite at Myanmar government gem auctions. Most of Myanmar’s Burmese rubies and sapphires are smuggled into Thailand to be cut and sold on the international market, and no embargo can change that.
Unheated gem rubies over 6 carats are exceptionally rare and command record prices. Burmese rubies are the rarest and most valuable. Top color stones from Madagascar, Tanzania, and Mozambique are beautiful but cannot compete with Burma rubies in terms of value.
Unlike diamonds, rubies are valued for their transparency. Occasional inclusion, even one you can see, is usually not a deal-breaker as long as the rest of the stone is crystal clear.
The price of a ruby is in direct relation to the rarity and quality of the stone.
Leon Mege, acting as your buying agent, will work directly with the most reputable gemstone dealers worldwide to guarantee the best value in the market.
The average 3-5 carat ruby ranges in price from hundreds of thousands to several hundreds of dollars per carat depending on its origin, treatment, color, clarity, and cut.
A top-color unheated Burma ruby can fetch hundreds of thousands of dollars per carat at an auction. A heated ruby of the same size and color will cost tens of thousands per carat. A too light or too dark heated, poorly cut, heavily included ruby with tint will cost only a few hundred per carat. A reconstituted or glass-infused ruby fetches a few dollars per carat. Synthetic rubies and red spinel used as ruby substitutes in cheap jewelry are practically worthless.
For centuries before scientific tools for gem identification were invented, red spinels and rubies were often confused. For example, the famous Black Prince’s Ruby in the British crown turned out to be a spinel when custodians took it out during cleaning.
Spinel is a magnesium aluminum oxide, while ruby is aluminum oxide. In ancient times the red spinels came from Balascia or Badakhshan in Northern India, where the name “Balas Ruby” originates.
Called “Geneva rubies” and sold by an unknown merchant in 1880, they were the first known rubies produced by flame fusion. Twenty years later, Auguste Verneuil developed a special furnace for making synthetic rubies on a large scale. Most people do not realize that synthetic rubies can be that old. They are stunned to find out that grandma’s 100-year-old ruby is a worthless fake. Synthetic corundum is very cheap, easily identifiable, and never used in fine jewelry.
Injecting molten leaded glass under high pressure into heavily included rubys’ fractures turns nearly opaque stones transparent. The treatment is not permanent and can be easily damaged. Glass-infused rubies are brittle and have no value, but they look more natural than synthetics. Leaded glass is a toxic substance that can affect health.
